Cbse class-10th notes science||control and coordination
Chapter-7 biology Control and Coordination
●All the living organisms respond and react to changes in the environment around them.
●The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli such as light,heat,cold,sound,smell,touch etc.
●Both plants and animals are respond to stimuli but in a different manner.
Control and Coordination in Animals
It is brought about in all animals with the help of two main systems:
(a)Nervous system
(b)Endocine system
Nervous system
◆Control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues.
◆Nervous tissue is made up of an organized network of nerve cells or neurons ,and is specialized for Conducting information via electrical impulses from one part to the body to another.
Receptor:Are specialized tips of some nerve cells that detect the information from the environment .These receptors are located in our sense organs .
◆Ear: •Photoreceptors
•Hearing
•Balance of the body
◆Eyes: •Photoreceptors
•Seeing
◆Skin: •Thermoreceptors
•Heat or Cold
•Touch
◆Nose: •Olfactory receptors
•Smell detection
◆Tongue : •Gustatory receptors
•Taste detection
Neuron:It is the structural and functional unit of nervous system.
Parts of Neuron:
(a)Dendrite:Acquired information.
(b)Cell body:Acquired information travels as an electrical impulse.
(c)Axon:Longest fibre on the cell body is called axon.It transmits electrical impulse from cell body to dendrite of next neuron.
Synapse:It is the gap between the nerve ending of one neuron and dendrite of the other neuron
Here electrical signal is Converted into chemical signal for onward transmission.
Reflex Action
Reflex action is quick ,sudden and immediate response of the body to a stimulus ,Eg,:knee jerk,withdrawal of hand on touching hot object.
Reflex arc:The pathway through which nerve impulses pass during reflex action is called reflex arc.
Respone : Responses are of three main types:
(a) voluntary:Controlled by forebrain
Eg;talking, writing.
(b) Involuntary:Controlled by mind and hind brain;Eg ,heart beat, Vomiting,respiration.
(c)Reflex action: Controlled by spinal cord E.g,withdrawal of hand on touching a hot object.
Need of reflex Action: In some situations such as touching a hot object,pinching etc.we need to act quickly, otherwise our body would be harmed .Here response is generated from spinal cord instead of brain.
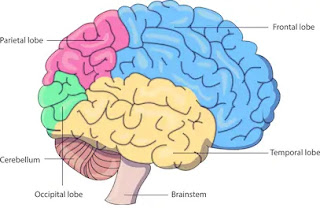
Human Brain
Brain is the main coordinating centre of the body.It has three major Parts:
(a)Fore-Brain (b)Mid-Brain (c)Hind-Brain
(a)Fore-Brain:It is the most complex or specialized part of the brain.It consists of cerebrum.
Functions:-
◆Thinking part of the brain.
◆Control the voluntary actions.
◆Store information (memory)
◆Receives sensory impulses from various parts of the body and integrate it.
◆Centre associated with hunger.
(b)Mid-Brain:Controls involuntary actions such as:
•Change in Pupil size.
•Reflex movements of head,neck and trunk.
(c)Hind-Brain:- It has three parts:
(i)Cerebellum:Controls posture and balance.Precision of voluntary actions e.g;Picking pen.
(ii)Medulla:Controls involuntary actions e.g;Blood Pressure,Salivation,vomiting .
(iii)Pons: Involuntary actions, regulation of respiration.
Protection of Brain and Spinal cord
(a)Brain:Brain is protected by a fluid filled ballon which acts as shock absorber and is enclosed in cranium(skull or brain box).
(b)Spinal Cord:Spinal cord is enclosed in vertebral coloumn.
Coordination between Nervous and Muscular Tissue.
Limitations of Electric Communication/nervous system:
(a)Electric impulse will reach only to those cells that are connected by nervous tissue.
(b)After generation and transmission of an electrical impulse,the cell takes some time to reset its mechanism before transmitting another impulse.So cells cannot continually create and transmit impulse.
(c)Plants do not have any nervous system.
Chemical Communication:To overcome the limitations of electric Communication.
Coordination in Plants
Movements in Plants:
(i) Independent of growth
(ii)Dependent of growth
(I) Independent of growth:Immediate respone to stimulus.
◆Plants use electrical -chemical means to convey information from cell to cell.
◆For movement to happen ,cells change their shape by changing the amount of water in them, resulting in swelling or shrinking of cells.
E.g,Dropping of leaves 'Touch-me-not' plant on touching it.
(ii)Dependent on growth:These movements are tropic movements I.e.., directional movements in response to stimulus.
◆Tendrils:The part of tendril away from the object grows more rapidly as Compared to the part near the object.This Causes Circulating of tendril around the object.
◆Phototropism:Movement towards light.
◆Geotropism:Movement towards/away from gravity.
◆Chemotropism:Growth of Pollen tube towards ovule.
◆Hydrotropism:Movement towards water.
Plant Hormones:Are chemical compounds which help to coordinate growth , development and respones to the environment..
Main plant Hormones are:
(a)Auron: ●Synthesized at shoot tip.
●Helps the cells to grow longer.
●Involved in phototropism
(b)Gibberellin:Help in the growth of the stem.
(c) Cytokinins: ●Promotes cells division.
●Present in greater Concentration in fruits and seeds.
(d)Abscisic Acid : ●Inhibits growth
●Cause wilting of leaves.
●Stress hormone
Hormones in animals:
Hormones:Hormones are the chemical substance which coordinate the activities of living organisms and also their growth.
Endocrine glands:These glands secrete their product (hormone)into the blood.
Endocrime Gland Hormones and their Functions
(1)Hormone:- Thyroxine
Endocrine gland :- Thyroid
Location:- Neck /throat region
Function:- Regulation of metabolism of carbohydrates,fats and proteins.
(2)Hormone:- Growth hormone
Endocrine gland :- Pituitary (master gland)
Location:- Mid brain
Function:- Regulates growth and development.
(3)Hormone:- Adrenaline
Endocrine gland:- Adrenal
Location:- Above both kidneys
Function:- Regulation (increasing) of blood pressure,heart beat, carbohydrate metabolism (during emergency)
(4)Hormone:- Insulin
Endocrine gland:- Pancres
Location:- Below stomach
Function:- Reduces and regulates blood sugar level.
(5)Hormone:- (a) Testosterone
(in males)
(b) Estrogen
(in females)
Endocrine gland :- (a)Testis
(b)Ovaries
Location:- genital/lower abdomen area
Function:- changes associatated with puberty (sexual maturity)
Iodised salt is necessary because
Iodine mineral is essential part of thyroxine hormone secreted by thyroid gland .Tyrosine regulates metabolism of carbohydrates,fats and proteins.So,we must consume iodised salt which is necessary for proper working of thyroid gland ,it's deficient causes a disease called goiter(swollen neck).
Diabetes
Disease in which blood sugar level increase .
Cause:Due to the deficiency of insulin hormone secreted by pancreas that is responsible to control blood sugar level.
Feedback Mechanism
The excess or deficiency of hormones has a harmful effect on our body.Feedback mechanism makes sure that hormones should be secreted in precise quantity and at right time.
E.g, Feedback mechanism to control the sugar level in blood is as follows:
Sugar level in the blood rises
↓






Comments
Post a Comment
Use the respectfully words in comment box.